Discover how AI-powered emotion detection technology is transforming emotional intelligence across industries. Explore insights, innovations, ethical concerns, and its future.
Unveiling the Power of AI in Emotion Detection
In today’s interconnected world, technology doesn’t just process information; it interacts with people on a deeply personal level. A trendsetter in this pursuit is artificial intelligence (AI), which has evolved from performing analytical tasks to understanding human emotions through emotion detection. This transformative capability is bridging the gap between humans and machines, enabling interactions that feel authentic, empathetic, and personalized.
Emotion detection is a subset of artificial emotional intelligence (AEI), focused on analyzing human emotional states using facial recognition, voice analysis, text sentiment, and even biometric data. From improving customer interactions to diagnosing mental health issues, emotion detection systems have become a cornerstone of innovation across industries. With its rapid adoption, AI is transforming emotional intelligence—the ability to perceive, understand, and respond to emotions—into a collaborative skill for both humans and machines.
Recent developments, particularly between November 18–20, 2024, highlight how powerful and significant this technology has become. Industry giants like OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft have unveiled advanced emotion-recognition tools that promise accurate, real-time emotional analysis. These innovations aren’t just tech improvements—they’re a glimpse into a future where machines and humans collaborate seamlessly for empathetic problem-solving.
Emotion detection changes the way industries operate—no longer are interactions transactional. Instead, they’re now driven by emotional insights. Healthcare, education, marketing, entertainment, and even law enforcement are undergoing radical transformations, thanks to real-time emotion analytics.
But every new technological advancement brings a set of challenges, and AI in emotion detection is no exception. Ensuring user privacy, eliminating bias in algorithms, and dealing with ethical concerns around consent and surveillance are essential steps that will shape its responsible adoption. Moreover, the technology raises important questions: Could humans rely too heavily on machines to understand one another? Will authentic human connections diminish in the process?
Over the next several sections, we’ll examine how AI-powered emotion detection works, dive into real-world applications, explore the challenges it poses, and forecast the role this disruptive technology will play in shaping our emotional realities. But first, let’s break down what emotion detection and emotional intelligence mean—and why they’re critically important in a digital-first era.
What is Emotion Detection and Emotional Intelligence?
To understand the significance of AI-powered emotion detection, it’s essential to differentiate between emotion detection itself and emotional intelligence (EI). Both concepts are intricately related, yet serve distinct purposes in the technological landscape.
What Is Emotion Detection?
Emotion detection is the technological ability to identify and analyze human emotions using advanced algorithms. These algorithms process data from facial expressions, body language, tone of voice, written texts, or biometric signals to infer emotional states. For example, an AI system reading a user’s facial expression might detect a smile and label it as “happiness” or “joy,” while one analyzing vocal patterns may identify stress or frustration from tonal shifts.
The aim of emotion detection is not just to collect data, but to derive actionable insights from it. Businesses use these insights to improve customer service, while educators use them to tailor teaching strategies for better learning engagement. Similarly, healthcare providers can leverage emotion detection to diagnose mental health concerns before they escalate—saving lives along the way.
Understanding Emotional Intelligence (EI):
Emotional intelligence, a term popularized by psychologist Daniel Goleman, refers to an individual’s ability to perceive, assess, manage, and influence emotions—both their own and others’. It is what helps us navigate relationships, handle challenges, and practice empathy in day-to-day life.
When integrated with AI, emotional intelligence creates a convergence of human empathy and machine efficiency. Think about chatbots that can sense when customers are frustrated and offer solutions accordingly, or virtual assistants that notice your stress levels through your voice and suggest calming activities.
The Convergence of AI and EI
By combining sophisticated AI systems with emotional intelligence principles, machines can move beyond transactional interactions to relational connections. AI systems enhanced with emotional intelligence are not only reactive but proactive. For instance, they can preemptively suggest solutions, empathize with users, and anticipate emotional needs, creating more meaningful engagement.
The integration of emotion detection into our everyday lives has spurred three distinct advantages:
- Empathy Enablement: AI systems can sense the emotional undertones of interactions, making them more empathetic.
- Engagement Optimization: Emotion-driven insights help tailor experiences for individual users, heightening relevance and satisfaction.
- Inclusive Communication: Emotion AI assists individuals who struggle with emotional recognition—such as those on the autism spectrum—enhancing interpersonal communication skills.
Emotion detection powers emotional intelligence to levels previously unimaginable. But while these technologies hold much promise, their rapid proliferation also brings new challenges that must be addressed responsibly.
Current State of Emotion Detection
As of November 2024, the pace of advancements in emotion detection technology is accelerating rapidly. This period has seen breakthroughs across various domains—from tools for healthcare and customer service to innovations in education and consumer devices. Let’s explore the highlights.
1. Enhanced Systems by Tech Leaders
Tech industry leaders like OpenAI, Microsoft, and Apple have rolled out updates to their emotion recognition systems this month. Microsoft’s latest platform integrates multimodal analysis, combining facial reading with voice synthesis for hyper-accurate identification of complex emotions. Meanwhile, OpenAI’s upgrade focuses on sentiment analysis, capable of interpreting sarcasm and nuanced emotional tones in textual content.
2. Wearable Adoption in Consumer Electronics
Consumer devices now include emotion-detecting wearables. Smartwatches with Emotion AI analyze heart-rate variability and skin temperature to identify emotional states like anxiety or excitement. Virtual reality (VR) headsets have emotion-sensitive features as well, creating simulations adapted to user emotions in real-time. For instance, VR applications provide relaxing virtual environments for stressed users or stimulate engagement in users exhibiting boredom.
3. Expanding Healthcare Integration
The healthcare industry stands out as one of the largest beneficiaries of emotion detection advancements. Recent breakthroughs enable therapists to track patients’ emotional well-being remotely. New AI tools can recognize signs of early depression based on facial expressions or inferred emotional data during telehealth sessions.
4. Education Gets a Boost
Emotion detection is transforming classrooms. AI can assess student engagement through facial expressions, postures, and even how they interact with learning content online. Systems reacting to signals of frustration or boredom adapt teaching methods instantly, improving information retention. Recently, AI-equipped courses introduced features that flag instances where students might need breaks or focused assistance.
5. Enterprise and Marketing Revolution
In businesses, emotion detection is now mainstream. From online chat applications to in-store facial recognition, businesses gain real-time emotional insights to tailor customer experiences. Sentiment AI platforms also analyze massive volumes of reviews and product interactions. For example, online retailers innovate their marketing pitches based on the emotional trends observed in user behavior metrics.
Emotion detection is no longer a concept but a reality shaping industries today. By combining technology with human interaction, these tools extend the possibilities of innovation across diverse fields. However, with such growth comes ethical dilemmas and new responsibilities, which we will discuss in later sections.
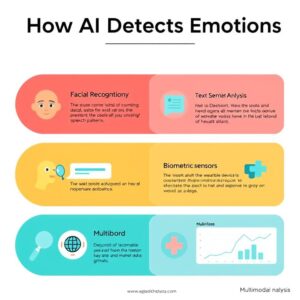
How AI Detects Emotions: Techniques and Technologies
Emotion detection systems are powered by cutting-edge AI technologies designed to analyze multiple human behaviors and physiological cues. These systems leverage machine learning models, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and even biometric tracking to decode emotional states with increasing precision. Below, we take a closer look at the key mechanisms that enable AI to “read” emotions.
1. Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition is one of the most widely used methods in emotion detection. It involves using computer vision algorithms to scan a person’s face for emotional clues. The human face has 43 muscles, and their movement creates microexpressions—subtle, involuntary facial expressions that reveal emotions. AI systems analyze these microexpressions, as well as macroscopic changes like smiles, frowns, raised eyebrows, or furrowed brows.
How it works:
The system first detects a person’s face in an image or video input. It then maps the facial landmarks (e.g., eyes, nose, lips) and calculates changes in the positions of these features. For example, a raised upper lip with tightened eyes may indicate disgust, while an upward curving of the lips signals happiness.
Modern emotion recognition tools, like the platforms released in 2024 by Google and Microsoft, rely on deep neural networks to train their models on diverse datasets, ensuring adaptability to various ethnicities, age groups, and even lighting conditions.
2. Vocal Emotion Recognition
Human emotions are often reflected in the tone, pitch, rhythm, and volume of speech. This is where voice recognition plays an essential role. By analyzing vocal features, AI systems can determine emotional states such as excitement, sadness, anger, or fear.
How it works:
Using NLP and acoustic signal processing, machines break down audio recordings into smaller components like frequency, amplitude, and modulation. By comparing these components to reference datasets of emotional speech patterns, the system identifies the dominant emotion(s) expressed in the speaker’s tone. For instance, a louder pitch with fast-paced speech may indicate anger or energetic excitement, while a slower and softer tone might signal sadness or exhaustion.
Companies such as Nuance and Verint are now incorporating vocal emotion detection into customer support and sales platforms, offering real-time feedback to agents as they engage with clients.
3. Text Sentiment Analysis
In digital conversations, emotions can be inferred not just through what is written but also how it is expressed. Text sentiment analysis allows AI to detect emotions from written communication by analyzing word choices, context, punctuation, and even emoji use.
How it works:
AI systems use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to break down sentences into smaller components, analyzing patterns in sentiment markers. For example, exclamations and positive adjectives (e.g., “I’m so thrilled!”) might indicate excitement, while negative markers (“I feel awful”) suggest sadness. Even subtle cues, such as the use of ellipses or a lack of punctuation, are interpreted for potential emotions like hesitation or insecurity.
This application has grown particularly powerful in social media monitoring and customer feedback analysis, where businesses like OpenAI have leveraged NLP models to track consumer emotions at scale.
4. Biometric Sensors
Beyond external cues, emotions are also reflected biologically, such as in heart rate fluctuations, skin conductivity, or body temperature. Wearables like smartwatches and fitness trackers use biometrics to detect emotional and physiological states in real time.
How it works:
Devices equipped with sensors collect data such as heart rate variability (HRV), which is closely tied to emotional responses like stress or relaxation. For instance, during anxiety, HRV decreases, skin conductivity increases, and sweat gland activity intensifies. AI algorithms analyze this data to generate emotional insights. Wearables from companies like Fitbit and Garmin, in collaboration with emotion AI startups, now provide personalized wellness recommendations based on detected stress patterns.
5. Multimodal Emotion Recognition
The latest evolution in emotion AI is multimodal analysis, wherein multiple data streams—facial, vocal, textual, and biometric—are combined for holistic emotional insights. For example, a system observing both facial sadness and matching sadness in vocal tones would have higher confidence in labeling the emotion as grief.
This integrated approach improves accuracy and eliminates ambiguities that may arise when relying on a single data stream. For instance, someone wearing a “poker face” may still betray frustration through their voice or body language, which a multimodal system would accurately interpret.
By advancing these techniques, emotion detection systems are becoming indispensable tools across industries ranging from health monitoring to customer engagement. As systems grow more reliable, their applications widen—but so do their potential ethical issues, which we’ll discuss in the following sections.
Benefits of Emotion Detection
AI-driven emotion detection has unlocked a new era of possibilities where technology no longer merely observes users but engages them empathetically. The benefits span industries and profoundly impact individual lives, offering opportunities to create smarter, user-centric systems. Below, we explore the ways in which emotion detection is driving substantial change.
1. Enhanced Customer Experience
One of the most prominent use cases of emotion detection has been in customer service and marketing. Emotion AI tools allow businesses to analyze customer interactions—collected from chat logs, voice calls, or live camera feeds—and identify emotional cues like frustration, happiness, or confusion.
For example, an AI-powered chatbot equipped with sentiment analysis can detect when a customer grows irritated by repetitive questions, prompting it to escalate the issue to a human representative. Similarly, voice tone analysis in call centers can alert agents when their tone becomes defensive, optimizing training and customer satisfaction.
2. Mental Health Support
Emotion detection is revolutionizing the mental health industry. Advanced AI models can monitor patients’ emotional states in real-time, detecting markers of anxiety, depression, or other mental health challenges. Remote therapy sessions now use sentiment AI to track fluctuations in patients’ emotional well-being over time, providing therapists with valuable insights.
Increased access to affordable, AI-powered support systems also bridges the gap for individuals living in areas with limited mental health professionals. Apps like Woebot and Wysa rely on NLP-based emotion detection to respond empathetically to users’ inputs while offering mood-boosting strategies.
3. Improved Education Systems
AI-powered emotion detection systems are shaping the future of educational technology. In classrooms, AI tools monitor students’ levels of engagement, frustration, or comprehension by analyzing their expressions during lessons. For remote learning, these tools ensure that educators remain attuned to students’ emotional needs, even through digital platforms.
When students appear frustrated, the system adjusts learning material or suggests breaks, making educational experiences tailored to each learner’s emotional state. As a result, these systems increase productivity, minimize anxiety, and foster long-term academic success.
4. Workplace Productivity and Morale
Organizations are applying emotion detection systems to monitor workplace well-being and team productivity. Tools that analyze employee sentiment in text communications, emails, or video meetings help companies detect drops in morale. For instance, tracking burnout indicators across teams allows managers to take proactive measures such as reducing workloads or prioritizing wellness programs.
5. Greater Accessibility for Individuals with Disabilities
Emotion AI is creating inclusive technology for individuals with disabilities. For example, AI-powered emotion detection tools offer people on the autism spectrum greater clarity in interpreting facial expressions or vocal inflections that may otherwise be difficult to distinguish. Similarly, wearable devices assist individuals who are visually impaired by providing audio cues about the emotional states of people nearby.
The benefits of emotion detection are substantial, making it a crucial technological development for improving human-centric solutions in the years to come. However, balancing these benefits with ethical and privacy concerns remains a critical challenge.
Ethical Concerns and Challenges
While emotion detection offers extraordinary advantages, it also raises complex ethical and practical challenges. These challenges revolve around data privacy, consent, algorithmic bias, and the potential misuse of such technologies. Without careful planning, the risks could outweigh the benefits.
1. Data Privacy Risks
Emotion detection relies on highly sensitive data, such as facial expressions, voice patterns, and biometrics. These datasets are deeply personal and, if compromised or mishandled, can lead to severe privacy violations. For instance, companies tracking users’ emotional states might use this data without consent or even sell it to third parties for targeted advertising. Similarly, surveillance systems could record expressions that reveal stress, anxiety, or other emotions without the individual even realizing it.
The recent conversations around privacy regulations, especially after data misuse scandals reported as late as November 2024, highlight the increased urgency in implementing robust data-protection protocols. Despite existing laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the United States, nuanced policies focused on emotion AI remain underdeveloped. Organizations need to focus on encrypting emotional data at all stages and should ensure that users provide informed consent before their emotional states are recorded or analyzed.
2. Consent and Transparency Issues
One of the biggest ethical concerns surrounding emotion detection is consent. Often, individuals may not even be aware that their emotions are being recorded and analyzed, creating a lack of transparency. For example, imagine walking into a retail store equipped with facial recognition cameras that scan your emotions as you browse products. While this data may help the store optimize your shopping experience, it may also feel invasive if you weren’t explicitly informed about the practice or allowed to opt out.
Transparency isn’t just a best practice—it should be a legal requirement. Clear disclosures about how emotion detection technology works, what data it collects, and how this information is used are essential to building trust with users. For emotion AI to thrive, users need full control over whether their emotional data can be collected or shared.
3. Algorithmic Bias and Accuracy
Emotion detection systems rely on machine learning models that are trained on datasets, but these datasets can often reflect the biases of their creators. For example, an AI system trained primarily on facial expression data from Western demographics might misinterpret emotional cues from individuals belonging to non-Western cultures. This is because emotions are not always expressed uniformly across different ethnicities, genders, or social groups.
Erroneous emotion detection outcomes due to cultural bias or limitations of the algorithm can have real-world consequences. In healthcare applications, biased tools could misdiagnose patients’ mental states. In law enforcement or hiring, false emotional interpretations could lead to unfair decisions. Companies and researchers must address these gaps by ensuring diverse and representative datasets are used in training emotion AI systems.
4. Manipulation and Emotional Exploitation
Perhaps one of the most controversial challenges is the potential for manipulation. Emotion detection capabilities allow advertisers and political campaigns to tap into users’ deepest vulnerabilities. For instance, knowing when someone is stressed, insecure, or fearful could be used to feed them ads designed to exploit these emotions, significantly increasing product sales or campaign success.
Such practices raise concerns about whether emotion AI is being used to empower or exploit individuals. A lack of strict regulations around emotional manipulation could lead to scenarios where businesses and organizations misuse this technology in ways that harm individual autonomy and mental health.
5. Surveillance and Authoritarian Misuse
There is a growing fear that emotion AI could be used as a mass surveillance tool, especially in authoritarian regimes. By embedding emotion detection systems into CCTV cameras or public interfaces, governments could monitor citizens and flag certain emotional cues as suspicious. For instance, a system might interpret frustration, anger, or distress as signs of dissent, leading to individuals being unfairly targeted for surveillance or punishment.
This level of surveillance raises ethical concerns about free expression, democratic freedoms, and the potential for these technologies to erode civil liberties. Governments and organizations must tread carefully to ensure that emotion AI is not weaponized against the public but instead used for constructive purposes.
Addressing Ethical Challenges
To counter these ethical concerns, various measures can be put in place:
- Stronger Regulations: Governments should enact laws focusing specifically on emotion AI, ensuring data privacy, consent, and ethical use are addressed comprehensively.
- Explainable AI: Emotion detection systems should be explainable, meaning developers need to provide insights into how their models arrive at conclusions. This transparency reduces the risk of misinterpretation.
- Data Minimization: Companies can adopt data minimization strategies, collecting only the emotional data necessary for specific purposes and deleting it afterward.
- Collaborative Oversight: Stakeholder collaboration—including researchers, ethicists, policymakers, and industry leaders—is vital to creating frameworks for responsible innovation.
By proactively addressing these risks, we can ensure emotion detection technology enhances human lives without threatening personal freedoms or ethical principles.
The Future of Emotion Detection
The future of emotion detection is brimming with possibilities, with the potential to revolutionize industries and transform how humans interact with technology. However, its trajectory will largely be shaped by advancements in technology, societal acceptance, and the ethical frameworks guiding its use. Here’s an in-depth look at where emotion detection is headed:
1. Advancements in Multimodal Systems
As emotion detection matures, the next big leap will come in multimodal systems —AI systems that integrate multiple data inputs. Imagine a tool that combines facial expressions, voice analysis, biometric signals (like heart rate), and contextual cues from text to deliver an in-depth emotional overview. By blending these inputs, mistakes caused by inaccuracies in a single channel can be mitigated.
For example, a teacher utilizing such a system during virtual classes could get a real-time analysis of whether students are stressed, disengaged, or actively participating, allowing for timely interventions.
2. Brain-Computer Interfaces
One of the most promising frontiers in emotion detection is brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). BCIs can directly interpret emotional states by analyzing brain activity. While still in its early stages, researchers expect BCIs to become mainstream within the next decade. For instance, they could be used to monitor mental health patients for signs of distress, even when physically unnoticeable.
3. Personal Emotional AI Assistants
With advancements in sentiment AI, personal virtual assistants could develop empathetic capabilities. A smart home assistant may detect sadness in your voice and suggest uplifting activities, or notice heightened anxiety and play calming music. These assistants will create more meaningful engagements and build trust with users, making technology an integral part of our emotional well-being.
4. Global Standardization and Ethical Governance
By 2028 and beyond, we’re likely to see global consensus on regulations governing emotion AI. Unified frameworks for data privacy and ethical use will ensure the technology is adopted responsibly across industries. AI models will also be audited and certified for transparency and fairness, particularly in applications like hiring, law enforcement, and mental health.
5. Integration Across All Industries
From healthcare to entertainment, emotion AI is expected to become ubiquitous. Imagine video games that adapt stories based on the player’s emotional reactions, or movie-streaming services that recommend content based on your current emotional state. In medicine, emotion detection could work alongside AI diagnostic systems, improving patient care through emotional insights.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is emotion detection in AI?
Emotion detection is the use of AI and machine learning to analyze and interpret human emotions through inputs like facial expressions, voice tones, written text, and physiological signals.
2. How accurate is emotion detection technology?
Accuracy depends on the data source and analysis method. While current systems achieve high precision in controlled environments, real-world factors like cultural differences or mixed emotions can reduce effectiveness.
3. How is emotion detection used in mental health?
Emotion detection aids therapists by tracking patients’ emotions, identifying early signs of depression or anxiety, and personalizing treatment plans. AI apps also provide emotional check-ins for users experiencing stress or mood swings.
4. Is emotion detection invasive?
It can be if deployed without user consent or transparency. Strong regulations and ethical guidelines are necessary to prevent misuse and protect personal data.
5. What industries are benefitting the most?
Healthcare, education, customer service, marketing, and entertainment are among the key sectors leveraging emotion detection for tailored service and improved outcomes.
6. Can emotion detection replace human emotional intelligence?
No, it can’t replace human empathy and understanding. Instead, it serves as a complement, enabling technology to enhance human-centric services.
Emotion detection stands as one of the most exciting technologies of the 21st century, with the potential to reshape how humans relate to machines and to one another. While its applications promise innovation across industries, the ethical and privacy concerns associated with it demand thoughtful and collaborative approaches. By prioritizing transparency, responsible use, and ethical frameworks, we can unlock the full potential of emotion detection technology, ensuring its positive impact on society for decades to come.